Automated Question Answering and SQuAD
Why Question Answering ?
Every other problem in the field of Natural Language Processing can be thought as an Question Answering problem ie Named Entity Recogtion (NER) can be thought as given a Sentence “S” what are the Named Entities in S.
In general by question-answering we will asume the task is to find given a question the algorithm or system should be able to produce a reasonable answer . The problem of Automated Question Answering can be of three different types ,
A. Reading comprehension
Reading Comprehension is a data driven approach where we are given a paragraph P and an question Q , our task is to find answer A of Q from the knowledge available from P . Like every other QA task this requires a lot of labeled data where the Paragraph , Question and Answer are given . Then we apply machine learning or statistical technqiues to build our model . Some of the most popular dataset in the task of Reading Comprehension is the BAbI Tasks by Facebook and the SQuAD by Stanford . In next section we will discuss about SQuAD in detail .
B. Open Domain QA
Open Domain QA where the answers are not in a limited paragraph but the knowledge required to answer the question needs knowledge from a large collection of documents .
C. Cloze Dataset
In this type of Dataset the task is to predict a missing entity given previous text in the same context , the advantage of this dataset is building such dataset is easy and requires less manual effort . But initally it was thought that solving this problem might be hard , but later performance was staturated and further performance gain was not possible. The difference of this from reading comprehension is that in Reading Comprehension the answer to the question is in the given paragraph , but here the content of the paragrah suggests the answer.
SQuAD
We present the Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD), a new reading comprehension dataset consisting of 100,000+ questions posed by crowdworkers on a set ofWikipedia articles, where the answer to each question is a segment of text from the corresponding reading passage
Stats
- 100,000+ Questions.
- 23,215 paragraphs for the 536 articles.
- Wide range of topics, from musical celebrities to abstract concepts.
- 80% training - 10% development - 10% test
Comparision With Similar Datasets
| Datset Name | Differnece | Link |
|---|---|---|
| MC Test | MC Test is RC , but Multiple Choice Answers | Link |
| WikiQA | Smiliarly collected but here the task is to select sentence but in case of SQuAD we select a span or segment from sentence | Link |
| BAbI | Very small and synthetically generated | Link |
Evaluation Metrics for SQuAD
Like every other Machine Learning task in the task of Question Answering we want to quantify how good our system is performing. To Do so we need some measures or metrics , Here we have metrics on which our models are judged those are
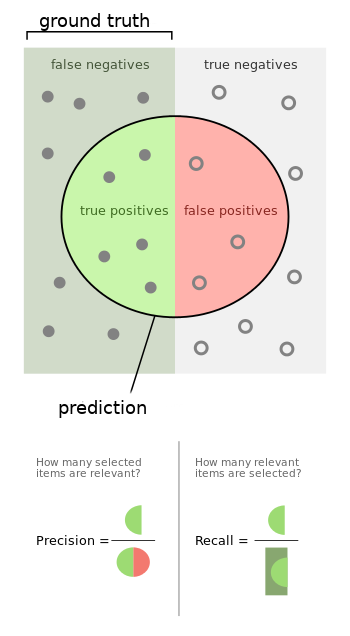
A. Exact match
This metric measures the percentage of predictions that match any one of the ground truth answers exactly.
B. (Macro Averaged) F1 Score
This metric measures the average overlap between the prediction and ground truth answer. We treat the prediction and ground truth as bags of tokens, and compute their F1. We take the maximum F1 over all of the ground truth answers for a given question, and then average over all of the questions.
Performance
| Type | EM Score | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 40.0% | 51.0% |
| Human | 80.3% | 90.5% |
Conclusion
In later parts we will see how to build a model for this task and various other models that resonabley for this task .